ReGradeTM FAQ
How will ReGrade help me find problems before I release new software?
Curtail ReGrade finds problems with new versions of software before that software is released to customers – we call this Digital PreCognition. With ReGrade, you can shift left or expand right to find defects earlier in the development cycle or right before release. ReGrade provides an automated way to tell how a new version of software will work in comparison to an existing version of the software. ReGrade does this without requiring any scripted testing. This patented technology provides developers, QA, DevOps, and release teams with an automated tool for evaluating release candidates using real production traffic or QA test traffic before going live.
Prior to release ReGrade helps you evaluate
• Software performance
• API changes
• 3rd party integrations
• Software supply chain components
• Refactoring old software code (i.e. making “what if” changes to an existing software application without any risk to its performance)
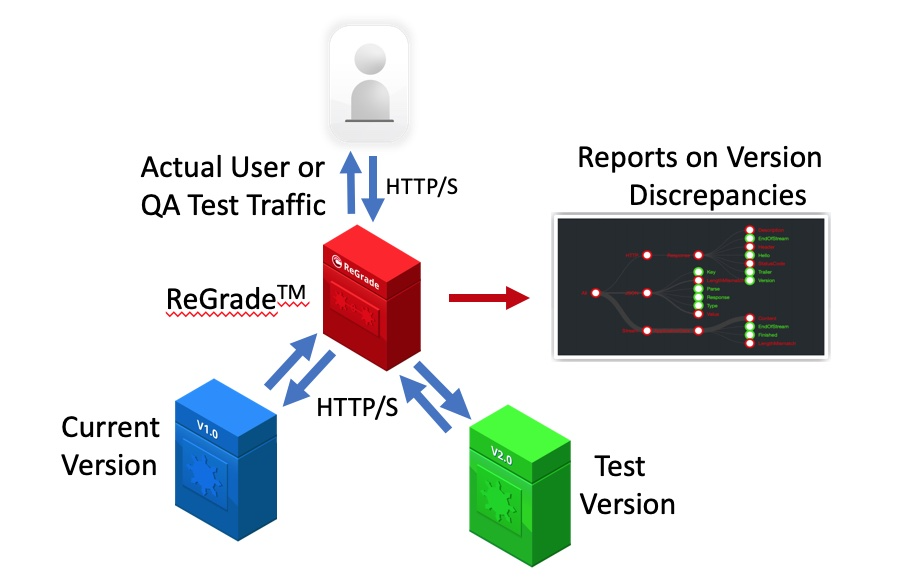
Figure 1. ReGrade compares two versions of software to find problems in the new version.
How does ReGrade work?
ReGrade compares a production software version and a release candidate by playing the same network inputs to both versions and observing the differences in responses. For the network inputs you can run live user data or test traffic through both versions of the software to determine where flaws are and how to fix them before releasing.
ReGrade’s patented method identifies differences from unexpected application behavior and configuration missteps prior to release. As in the movie Minority Report in which the PreCogs can see crimes ahead of time, ReGrade’ Digital PreCognition shows how the new software version will run once it is released before it is released. Like looking into a network crystal ball, this capability is a very powerful tool for observing the behavior of the new software as if it had already been released and/or seeing problems much earlier in the release cycle. ReGrade analyzes the responses from both the production and release candidate software versions and reports any differences. Those differences might be bugs, configuration issues, or performance problems.
When ReGrade finds a difference in the way a production software version and a release candidate respond to the same input, it will display that difference. ReGrade will also provide actionable information about the cause of the problem. With the detailed, actionable information, bugs will be easy to find and fix. This method of testing will find issues that had not been contemplated by scripted testing regimens. It will find zero-day bugs (unknown unknown bugs) not found before in addition to finding bugs that are expected to be found by normal testing.
Can ReGrade funnel live production traffic from the running, production version of the software to the test version to evaluate a release candidate?
Yes. It is easy to configure ReGrade to send a copy of any traffic coming to the production version of the software to the new release candidate. The real production end users only interact with the production version. When using ReGrade with live user data, ReGrade’s intelligent comparison engine does not disrupt the end user experience. Production end users are completely isolated from the tests ReGrade is conducting.
Behind the scenes, ReGrade is also passing the real end user requests to the release candidate version. ReGrade will report any differences in the way two versions of software handle inputs. ReGrade will document any difference in the network traffic generated by the two software versions.
Does ReGrade work in environments with a backend database?
Yes, ReGrade works in software configurations utilizing database backends. In the case below where the software writes data into a database, only the production version will handle the database interaction. ReGrade will continue to compare the traffic to and from the database looking for ways in which the release candidate version of the product might have introduced an unexpected change.
ReGrade can compare software behavior of the full transaction to the backend database or other services. This allows you to compare software behavior without duplicating external services and storage layers, including databases. It also enables DevOps to look for database deadlocks.
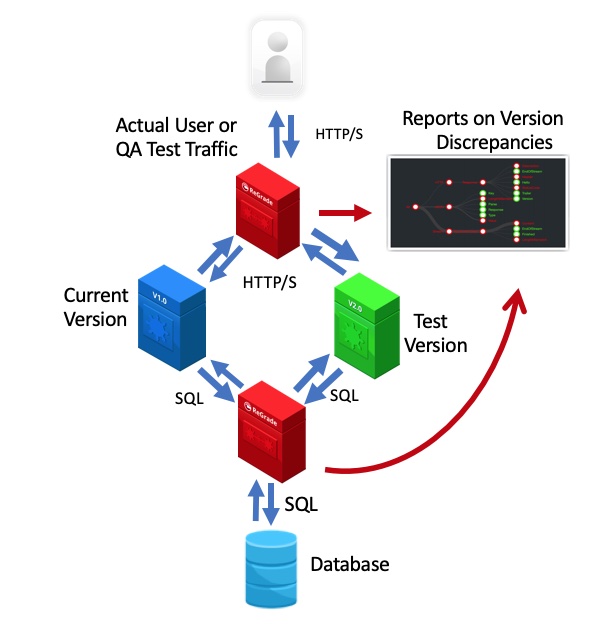
Figure 2. ReGrade running with a backend database.
Can ReGrade find supply chain attacks and supply chains problems?
Yes. Recent, highly publicized attacks on widely distributed software components have made everyone more aware of the possibility of cyberattacks on software supply chains. Current detection mechanisms (IDS, IPS, vulnerability scanning) are unable to find these problems, but Curtail ReGrade can detect server-side supply chain security issues. If malicious code has been inserted into a component of the software supply chain, it will ultimately create differences in the way the final application behaves.
ReGrade can compare how an application behaves with different versions of the underlying components. When ReGrade finds discrepancies between underlying component versions, this can indicate malicious code or some other defect has been inserted in the software supply chain. ReGrade will display exactly which application request caused the difference in behavior, making it straight forward to find the underlying cause.
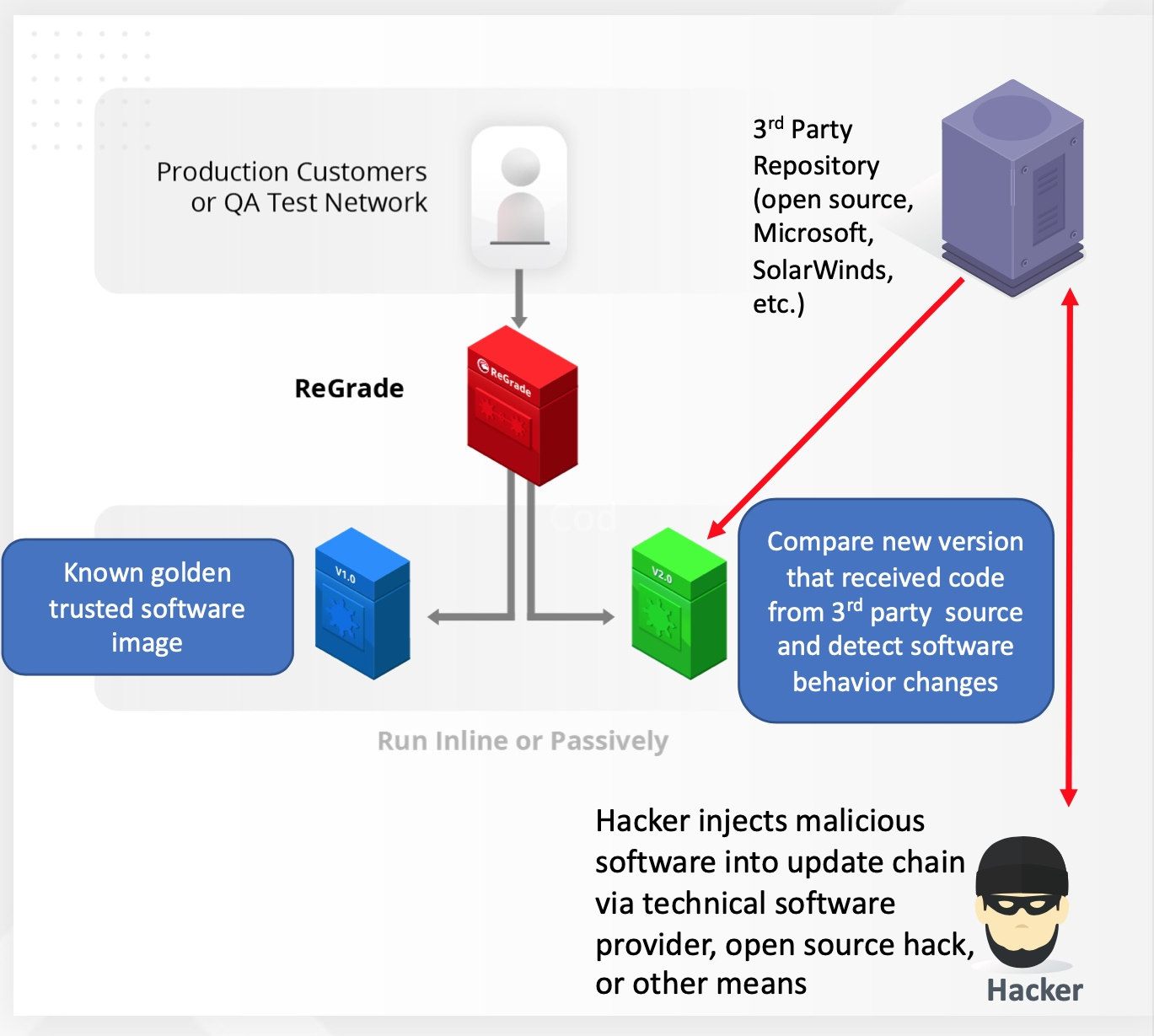
Figure 3. ReGrade can find malicious code in software supply chains.
Many build systems pull from open source repositories at every build, and will use the latest version available at build time. Common open source repositories that use this pattern include NPM, RubyGems, and PyPI. Because the actual software served by these open source repositories can change at any time, there is no guarantee that a build today won’t have unwanted changes compared to a build yesterday.
Examples include https://blog.sonatype.com/malicious-dependency-confusion-copycats-exfiltrate-bash-history-and-etc-shadow-files and https://www.theregister.com/2016/03/23/npm_left_pad_chaos/
ReGrade can catch these changes that might otherwise go undetected.
What happens when new functionality is added to a software version?
Functional regressions are when some modification in software leads to failures in the functionality of an application. Like other regressions, they are unintended side-effects of changes to the software. ReGrade identifies all of the actual behavioral changes observed between two software versions or packages by giving them the same inputs and identifying all of the differences in the outputs. These can be conveniently summarized based on common requests or common differences in responses. Intended changes can be catalogued and compared with the complete set of changes, and any functional regressions will then stand out as the unexpected changes.
How would ReGrade help test a software product that is not yet in production? Can we shift left in our development lifecycle?
Curtail ReGrade testing allows you to shift left in your development cycle, catching unexpected changes sooner, including in development and QA stages. Individual developers can use ReGrade to validate that their changes are impacting the software behavior as they expect, and QA can use ReGrade to validate that the software changes match the expected changes for the milestone.
If I test with live user traffic, will the end users know about the test version?
No. The production end user only sees the response from the current production software version. They will be unaware that the interactions they have with the production software version are also being fed to the release candidate for testing purposes. Only those running ReGrade behind the scenes will know that user traffic is being duplicated to test the release candidate.
Can ReGrade use existing simulated or test traffic to help me find bugs in the new release candidate?
Yes. ReGrade can play test traffic against the new software version and evaluate any differences between how the production version responds to the test traffic vs. how the new release candidate responds to the test traffic.
You can also record manual tests and play them back at line speed and see what differences have been introduced.
Can ReGrade run the same traffic over and over against new test versions?
Yes. ReGrade can record any inputs sent to the new software version for future playback against new versions of the software. This part of the product is called ReGrade RePlay. ReGrade RePlay takes a known test and replays it against a development version of the software, so you can evaluate the behavior of the new version against the existing baseline (test) version. Developers can run the test against versions still underdevelopment, or QA can use ReGrade RePlay to speed the testing process of release candidates before they go out the door.
ReGrade can also analyze how any QA scripts would work when compared to the new version of the software under consideration.
How does ReGrade pinpoint the location of a bug and provide Root Cause Analysis?
ReGrade gives developers pinpoint information about what behavior in a release candidate creates a difference compared with the existing, production version. ReGrade can identify the exact behavioral changes that occurred and provide detailed information about the interactions with the network service that led to the unexpected result. ReGrade gives the precise requests that caused the software bug, security anomaly, or poor performance. Developers then know exactly where to go to fix the problem and what to fix.
The comparison result is a unique and different piece of data that tracks side-by-side performance and the network response, mapping and tracing the various ID’s to find any differences that could indicate a problem.
The example below shows a LengthMismatch between two versions of software. The first figure is the topology of possible errors that ReGrade can display. Here the ReGrade test returned a LengthMismatch error.
The error caused Personally Identifiable Information (PPI) to be leaked, which could be exploited by hackers. The second figure contains the detailed data ReGrade presents so that developers can find and fix the bug. The ID of the sensor involved and the query string request are shown.
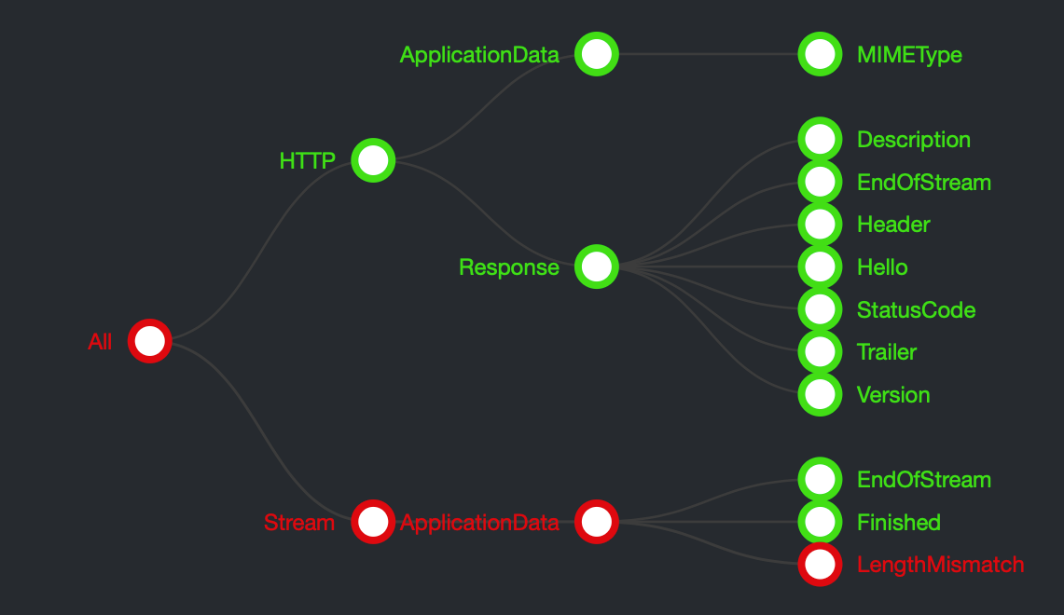
Figure 4. ReGrade Reporting Interface

Figure 5. ReGrade Root Cause Analysis Information
How does ReGrade keep the responses from the software production version in sync with the release candidate version being tested?
ReGrade uses patented technology to keep all of the session IDs in sync throughout the entire transaction.
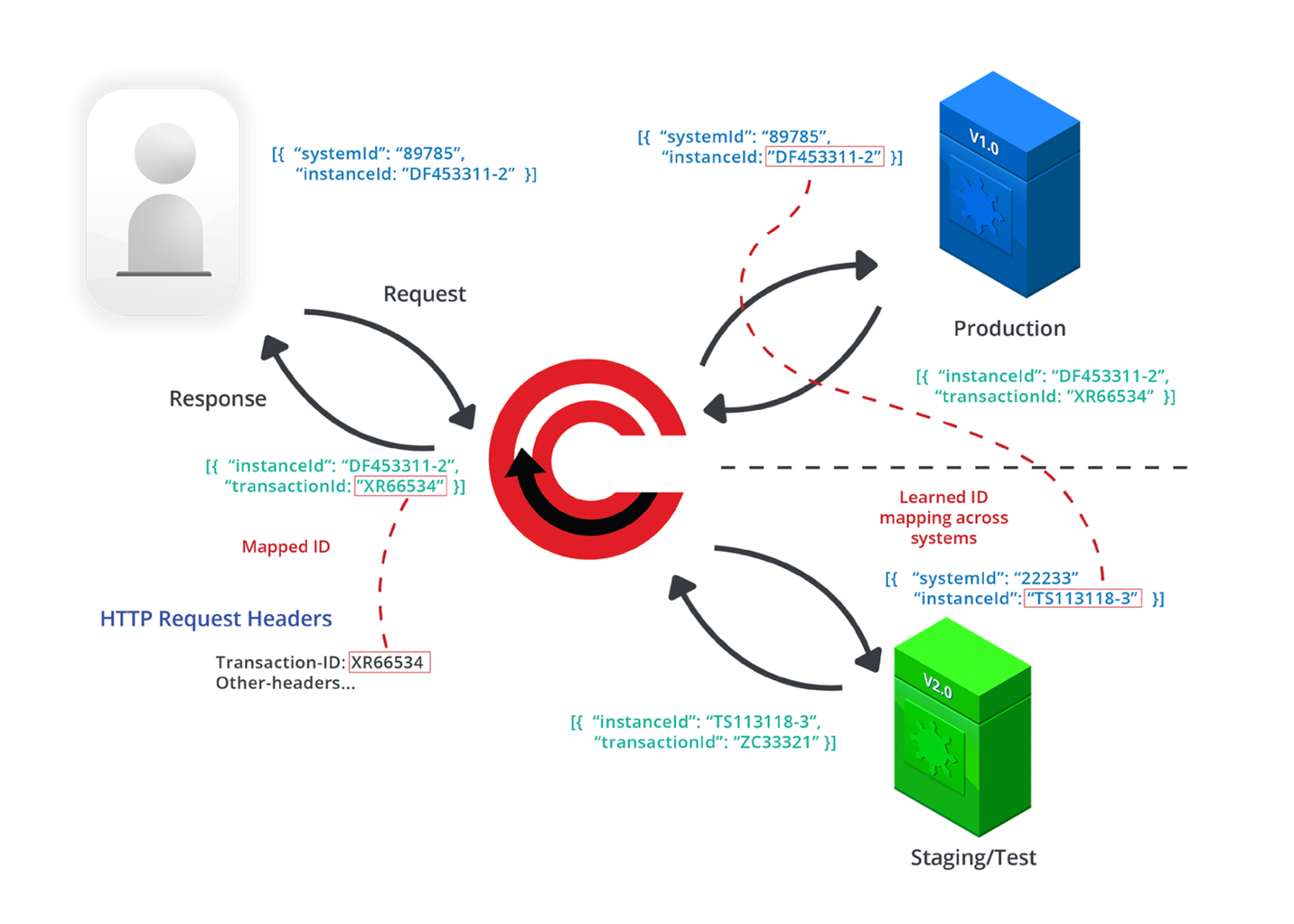
Figure 6. ReGrade’s Patented, Synchronized Session ID Mapping
How can ReGrade be used to monitor the performance of a software system?
ReGrade looks at a byte-by-byte comparison of two versions of the same application. In doing so, it documents the performance characteristics of each version over time. For each request to each application version, ReGrade tracks the amount of elapsed time required for the response. By comparing the response times between the versions for the exact same request, ReGrade shows what the response time differences are. The performance results are displayed numerically and graphically. ReGrade thereby allows you to see performance degradations and address them before release.
How does ReGrade compare with common APM (Advanced Performance Monitoring) solutions?
ReGrade can find unexpected performance changes with specific detail and lists of the requests and responses that caused the performance degradation. Conventional, log-based APM solutions are after-the-fact, meaning the event that caused the performance problem has already occurred (or is likely to occur from trending). ReGrade catches these defects sooner and proactively, before they go into production.
Implementation of ReGrade
How does ReGrade fit into my software environment?
ReGrade can be run on-prem or in the cloud. Customers can download and run the small container footprint image (<25MB image), either directly on-prem or within a private or public cloud environment. Configuring and running comparisons with Curtail ReGrade is straightforward:
• Configure and deploy the container image in minutes in the cloud or on-prem
• Read the configuration from a database
• Instantaneously examine detail-rich reports on changes between and among versions as test suites run, or go back in time to look at past differences
• A perfect comparison tool for DevOps teams, deploy Curtail ReGrade in CI/CD test and production environments, thereby enforcing regression test requirements before deployment
Environments Supported and System Requirements
• ReGrade can run anywhere Linux containers are supported, e.g. on Ubuntu and CoreOS.
• Easily deployed on premises or in the cloud, in VM’s or containers. Curtail has been deployed on physical hardware, VMWare ESXi, SAP Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure DevOps, and Amazon AWS Fargate and Elastic Kubernetes Services (EKS).
• Container image integrates easily with Kubernetes, Swarm, Fleet, Cloud Foundry, or Mesos.
• Deployment can be easily automated with third-party tools such as docker-compose, Amazon CloudFormation, Kubernetes deployments, Fargate, Cloud Foundry manifests, or Helm charts.
• Web services based on Node, Microsoft WCF, Apache, Spring MVC, and others
• Exportable to third-party tools (PcapNG, Syslog, CSV)
• <25MB footprint
What is the cost (in terms of resources) and performance impact of monitoring live traffic using Curtail?
Curtail ReGrade requires a PostgreSQL database, the user interface, and the sensor process to run. There is also additional network traffic introduced to communicate with the software under test, which is free under many common deployment models in popular cloud providers. When the sensor is run in “inline mode,” a small 1-2ms increase in end-to-end latency is likely.
ReGrade can be run in passive mode to avoid any additional latency.
Does ReGrade work with Cloud implementations?
Yes. ReGrade can be run in Cloud environments. ReGrade supports VMWare ESXi, SAP Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure DevOps, and Amazon AWS Fargate and Elastic Kubernetes Services (EKS).
Contact Curtail today for additional information, demo or a free trial. Call us at 805-880-1268. Email us at info@curtail.com. Or visit www.curtail.com
This document is provided for informational purposes only. This document is not warranted to be error-free, nor subject to any other warranties, whether express orally or implied. The technologies, services, or processes described herein are subject to change without notice.
